VMT Pharma Soft Sol Pvt. Ltd., headquartered in Hyderabad, India, offers an advanced Quality Management System (QMS) software built exclusively for the pharmaceutical and life sciences sectors. Our intelligent eQMS automates every stage of your quality lifecycle — from change control, CAPA, and deviation management to audits and vendor qualification. Designed to meet global regulatory standards (USFDA 21 CFR Part 11, EU Annex 11, GMP, ISO 9001), VMT QMS ensures compliance, efficiency, and continuous improvement across all operations.
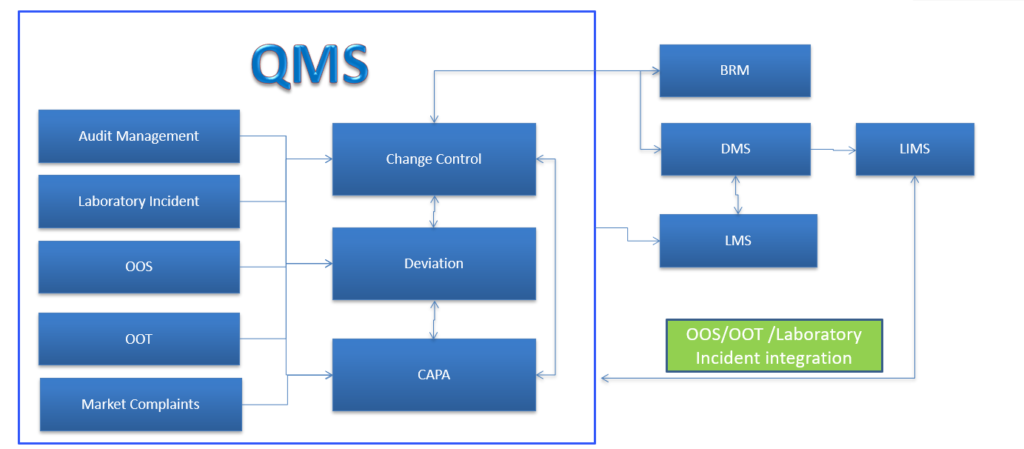
Quality Management System (QMS) is a set of procedures and practices that contribute to product quality. It targets individual processes and personnel involved in product manufacturing and prevents them from drifting away from quality standards.
Change control is required to lay down a procedure to control, manage, track and implement the proposed changes to the approved documents / procedures / validated analytical methods, facilities, equipment, software etc.
This standard process ensures that all the changes affecting any aspect of testing are appropriately reviewed, assessed and approved.
Deviation Management System module is an effective tool to find out the root cause of the deviations in an organization and ensure continual improvement is undertaken in a timely and effective manner.
CAPA provides a sequence of steps for identification, creation, tracking, implementation and monitoring to ensure the continuous improvement of the system and to prevent the reoccurrence of deviations or any un-expected circumstances notified through QMS elements.
The first stage involves discovering the root cause of the problem in order to identify an appropriate solution.
This stage involves analyzing the impact of the deviation on the quality of the product. This helps in determining the magnitude of the problem.
The next stage involves defining a CAPA which includes corrective actions to solve the problem and preventive actions to avoid recurrence of the problem.
Market Complaint module in eQMS Software, intended to file a complaint from the customer and acknowledge and identity the root cause and verify the analysis and getting closure by reporting to the customer.
Lab Incident module in eQMS Software, intended to guide and track the execution of an activity that needed as a Lab Incident to address a complaint, Deviations, Changes, Quality event or audit findings and ensure that CAPA with GxP impact are properly documented, approved and implemented by the departments within the organization
Internal Audit module in eQMS Software, intended to guide and track the execution of an activity that needed as a corrective and preventive measures to address a complaint, Quality event or audit findings and ensure that CAPA with GxP impact are properly documented, approved and implemented by the departments within the organization.
OOS occurs when the limits do not fall within the stipulated metrics. Out Of Specification module in eQMS Software, follows authorized procedures that ensure organizations comply with established regulatory standards of authorities
OOT module in eQMS Software, intended to guide and track the execution of an activity that needed as a corrective and preventive measures to address a complaint, Quality event or audit findings and ensure that CAPA with GxP impact are properly documented, approved and implemented by the departments within the organization.
VMT Soft Sol Pvt. Ltd. specializes in eQMS Software for the pharmaceutical industry. We simplify compliance, enhance efficiency, and ensure operational excellence.
# 8-3-167/A/52, 2nd Floor, Vani Nilayam, Vikaspuri, AG Colony Road, S R Nagar(PO), Hyderabad-500038.
Phone Number : +91-9866968830
